The positive impact of clean energy is undoubted and continues to grow stronger every day. When we talk about renewable energy we usually think mainly about alternatives such as wind or solar. But, the energy of waves, ocean currents and tides has also come into play.
Tidal and wave energy are what convert the movement of the waters of our seas into energy. It is collected through various mechanisms, from meticulous hydraulic systems installed on the coasts when the tides change height (tidal), to those that take advantage of the waves on the surface and systems similar to wind power that instead of the wind take advantage of the movement of the water in marine currents (wave currents).
Spain, for its part, has made great progress in this particular area. Among them, the implementation of the first tidal power plant in the world stands out, which after 9 years of operation continues to bear fruit.
SPAIN HAS THE FIRST COMMERCIAL TIDAL POWER PLANT IN THE WORLD
Located in Motrico (Guipúzcoa) and functional since July 2011, this plant has 16 turbines capable of producing 600,000 kWh per year . It has a capacity equivalent to the energy consumed by approximately 600 people.
This great step in the use of sea energy began to take shape 15 years ago. It was in 2005 when work began to reform the port of Motrico, adding this facility within the new breakwater.
The technology used by this type of system is known as Oscillating Water Column or OWC in its English acronym. One of the technicians explains its operation in more depth:
“When the wave reaches the dam, the water rises through the interior of the chambers, compressing the air they contain and expelling it through a small opening at the top. The air comes out at high speed and causes the alternator to rotate. «In the same way, when the wave retreats, it sucks air through the same hole, moving the turbine again and generating energy again.»
Given the variations in meteorological conditions, this particular system requires dynamic management especially when storms occur; When a large wave arrives (6 to 20 meters), the turbines should be regulated or in an extreme case turned off so that the plant does not suffer any type of damage.
TIDAL AND WAVE POWER PLANTS INSTALLED AROUND THE WORLD
Although both modalities take advantage of waves for energy production, tidal and wave energy are two different sources . As explained above, tidal energy is obtained through the difference in the height of the tides, while wave energy is obtained through sea waves and their movements.
Spain is not the only country that has proven the benefits of these alternatives. Facilities of this type are also located in:
- Bay of Funday, Canada.
- Chansy, France.
- Patagonia, Argentina.
- Passamaquoddy and Cobscook Bays, United States.
- Mezen Bay, Russia.
- Onchón, Korea.
- Walcott, Austria.
- River Severn, United Kingdom.
SPAIN’S POTENTIAL IN TIDAL ENERGY
Tidal energy in Spain has the potential to produce 8 times more energy than all renewables combined , which could translate into about 800,000 gigawatt-hours (GWh) per year, while the rest of the renewables would only reach approximately 100,000 GWh. . It certainly looks promising.
However, this is nothing more than speculation at the moment. Its high costs make it not entirely attractive to the market, which is currently reflected in the lack of development and research that has been done on this type of energy.
However, several European countries have made large investments in a new project called RealTide , started in 2018, and with an estimated duration of 3 years. The aim is to thoroughly study the failure of the turbines and develop new designs to improve vitally important components such as the blades and the energy conversion system.
Its mission is to perfect the system to get more out of it and reach the 800,000 GWh that are being talked about and, in turn, achieve a significant reduction in the costs intended for its implementation.
POSSIBILITIES IN THE STRAIT OF GIBRALTAR
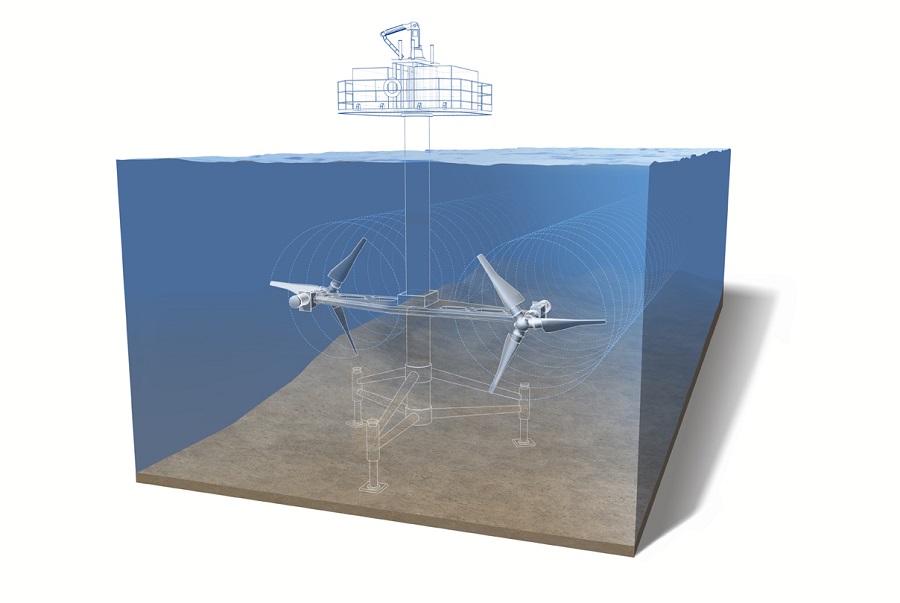
As has been emphasized, Spain has enormous potential, and its strongest point is in the Strait of Gibraltar. As the manager of Magallanes Renovables explains to Periódico de la Energía , Spain would be in a position to turn off all nuclear energy in the country, if appropriate tidal technology such as that of the ATIR platform is implemented.

Magallanes Renovables has large projects planned around the world, but thanks to the unique potential of this area, it began developing the ATIR platform in 2009. After having gone through a series of tests and requirements, this 8 million euro project It managed to supply between 1,000 and 1,500 homes that year .
ATIR works with turbines, in a very similar way to a wind platform. This can be installed anywhere in the world, as long as it is at least 30 meters deep . It has a remote control system, and was built in such a way that it does not do any harm to the environment. In addition, it can be easily accessed when an inspection is required.
IMPACT OF THE IMPLEMENTATION OF NEW ENERGY SOURCES IN CURRENT MARKETS
New energy sources mean, in turn, new possibilities for growth in the business world. However, this also implies that certain commercial sectors may see their production levels affected. A clear example of this is evident with fossil fuels, which used to cover all energy generation.

The green impact in the workplace has also been positive.
Renewable energies have proven to be employing more and more people and even exceed the number of people dedicated to fossil energy industries.
On the other hand, it is quite evident that investors will not miss the opportunity to change their objective, now betting their money on energy alternatives that could cover the gigawatts necessary to supply the entire world in the future.
Electricity generation from tidal energy is very promising, but still requires time, research and investment to mature and operate in an optimized manner and on a global scale.
However, we are not far from seeing how an enormous change in this commercial sector will be present, starting with Europe, a continent that has been investing significantly in this type of energy.
The incorporation of tidal and wave energy, along with photovoltaic and wind energy (which have already been very present for some time) makes it probable that, in a few years, some countries will be able to say goodbye to fossil energy. Maybe even permanently. It is a matter of time to witness the revolution that renewable energies will bring us in the near future.